With Liz Truss taking over as the Prime Minister of Britain, she became the third female to do so. Before her, Margaret Thatcher from 1979 to 1990 and Theresa May from 2016 to 2019 were given this responsibility under the reign of Queen Elizabeth II.
Since all laws in England are enforced in her name, Queen Elizabeth II cannot be charged with any crime. However, reigning is not the same as ruling. The prime minister is responsible for performing that responsibility and, incidentally, can be charged with a crime. Who then has greater power? The prime minister or the monarch?
Meet Liz Truss: The Third Female Prime Minister Appointed By Queen Elizabeth II
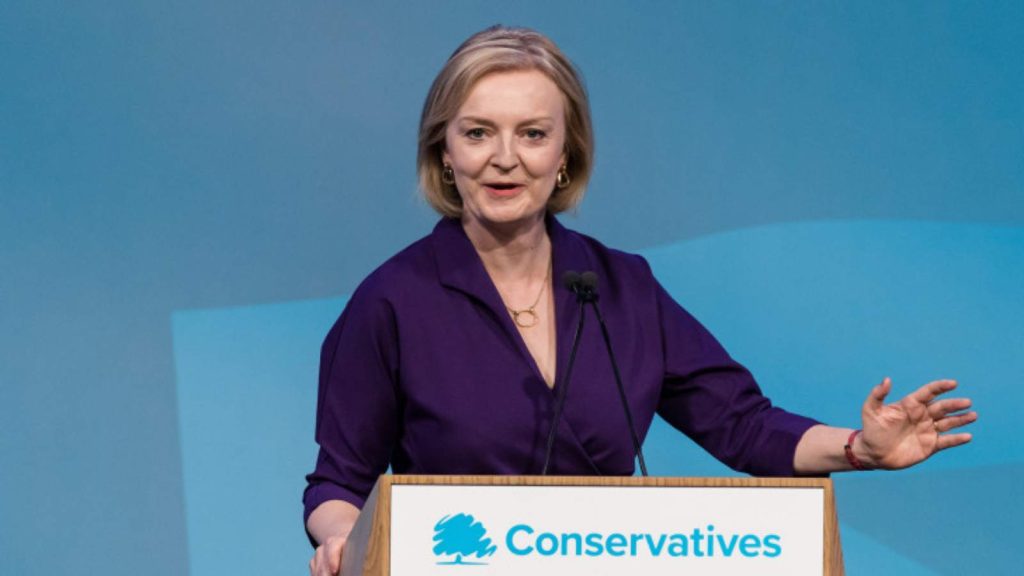

On September 6, the UK’s new prime minister was appointed. The 47-year-old British lawmaker Liz Truss won the key elections by 20,000 votes over Rishi Sunak. Truss assumed leadership of the Conservative party and seized control during a time of national emergency. Truss spent her time at the finance ministry concentrating on reducing taxes and dismantling bureaucracy. Until September 15, 2021, she served as secretary of state for foreign, Commonwealth, and development affairs. On September 10th, 2019, she was appointed Minister for Women and Equalities. In 2020, she won a seat as the southwest Norfolk district’s Conservative MP.
At Merton College in Oxford, Elizabeth pursued studies in philosophy, politics, and economics. Truss was sworn into office in 2010. In September 2012, she was named Parliamentary Under Secretary of State for Education and Childcare. From July 2014 to July 2016, Elizabeth was the Secretary of State for Environment, Food, and Rural Affairs. She had previously served as Deputy Director of Reform. She is a trained management accountant and has ten years of experience working as a commercial manager and economics director in the energy and telecom industries.
Read More: Queen Elizabeth II Net Worth: How Much Wealth Does The Monarch Of England Have?
Prime Minister Or Queen Elizabeth II: Who Holds More Power?

The term “royal prerogative” refers to a spectrum of executive privileges enjoyed by the reigning monarch. The monarch has the authority to call or suspend Parliament, grant or revoke passports, and even declare war, though these powers are rarely exercised (most problems are handled by Her Majesty’s nominated ministers). Queen Elizabeth can choose or remove the prime minister while she is still the monarch, but she is never allowed to vote or be detained. She cannot alter the line of succession to the throne and is only permitted to practice the Church of England as her faith.
16 nations are included in the constitutional monarchy of Queen Elizabeth, including Australia, the Bahamas, Canada, and New Zealand. Japan and Sweden are two other nations that are constitutional monarchies with kings or queens that have constrained authority. Queen Elizabeth is the head of state for the United Kingdom. She is entitled to consultation, encouragement, and warning, but she must follow the guidance of her governors, even if she disagrees with them. She does, however, still have the exclusive authority to veto any law she finds to be improper. When all things are considered, it appears that the queen is more powerful than the prime minister because she has the ability to fire the prime minister while he or she is unable to do the same to her.
Read More: Queen Elizabeth II’s Role Formally Rewritten Amid Health Concerns: All You Need To Know