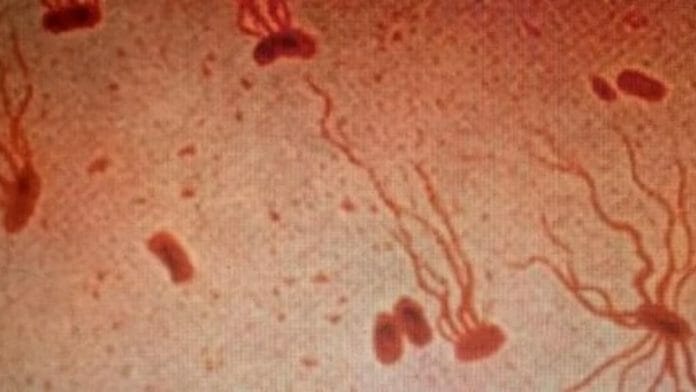
Even though typhoid fever is not as frequent in developed societies as it once was, the ancient threat that has been there for millennia is still a threat in today’s world. According to the findings of a new study, the bacteria that are responsible for typhoid fever are quickly replacing strains that aren’t resistant to the disease.
At this moment, antibiotics are the only treatments that are capable of effectively curing typhoid fever, which is caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S Typhi). Over the course of the previous three decades, the bacterium’s ability to withstand oral antibiotics has increased and become more widespread.
Read More: Why Do Some People See And Hear Dead People? Scientists May Have An Explanation
Typhoid Strains That Are Resistant To Antibiotics Are A Cause For Concern
S. Typhi’s rapid emergence and dissemination in recent years is worrisome, according to Stanford University infectious disease expert Jason Andrews. It underscores the necessity of rapidly increasing preventative efforts, particularly in countries at greater risk.
Viral News states that scientists have been warning for years about drug-resistant typhoid strains, but this study is the most complete genomic analysis of the bacteria to date. Third-generation antibiotics including cephalosporins, macrolides, and quinolones have traditionally been used to treat most XDR typhoid strains.
Quinolone-resistant bacteria accounted for more than 85% of all cases in Singapore, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Bangladesh by the early 2000s. Cephalosporin resistance was also on the rise during the same period.
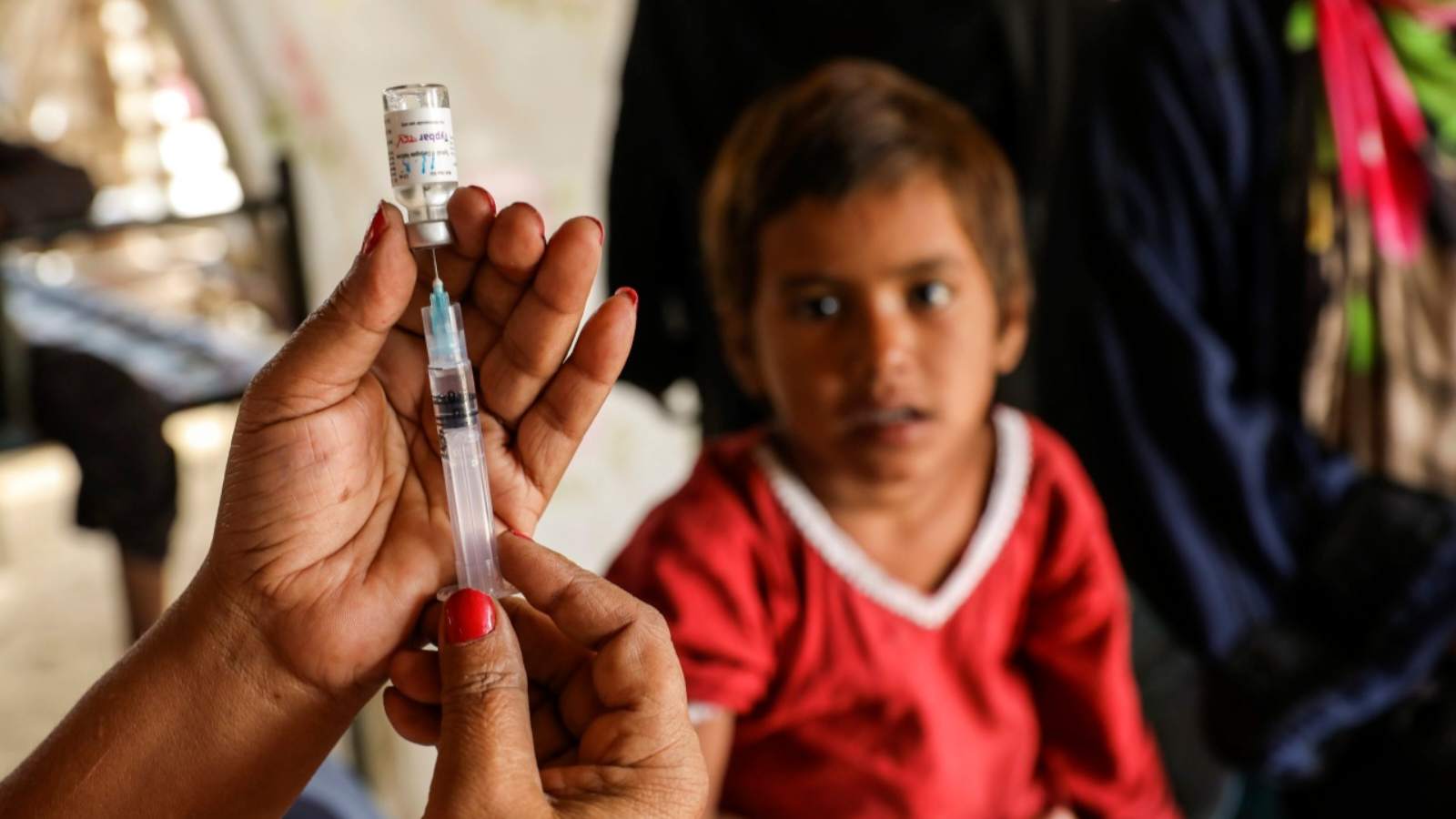
Typhoid Conjugate Vaccines Could Prevent More Outbreaks In The Future
The efficacy of oral antimicrobials for the treatment of typhoid has been threatened by the emergence of azithromycin-resistant mutations, according to this recent study.
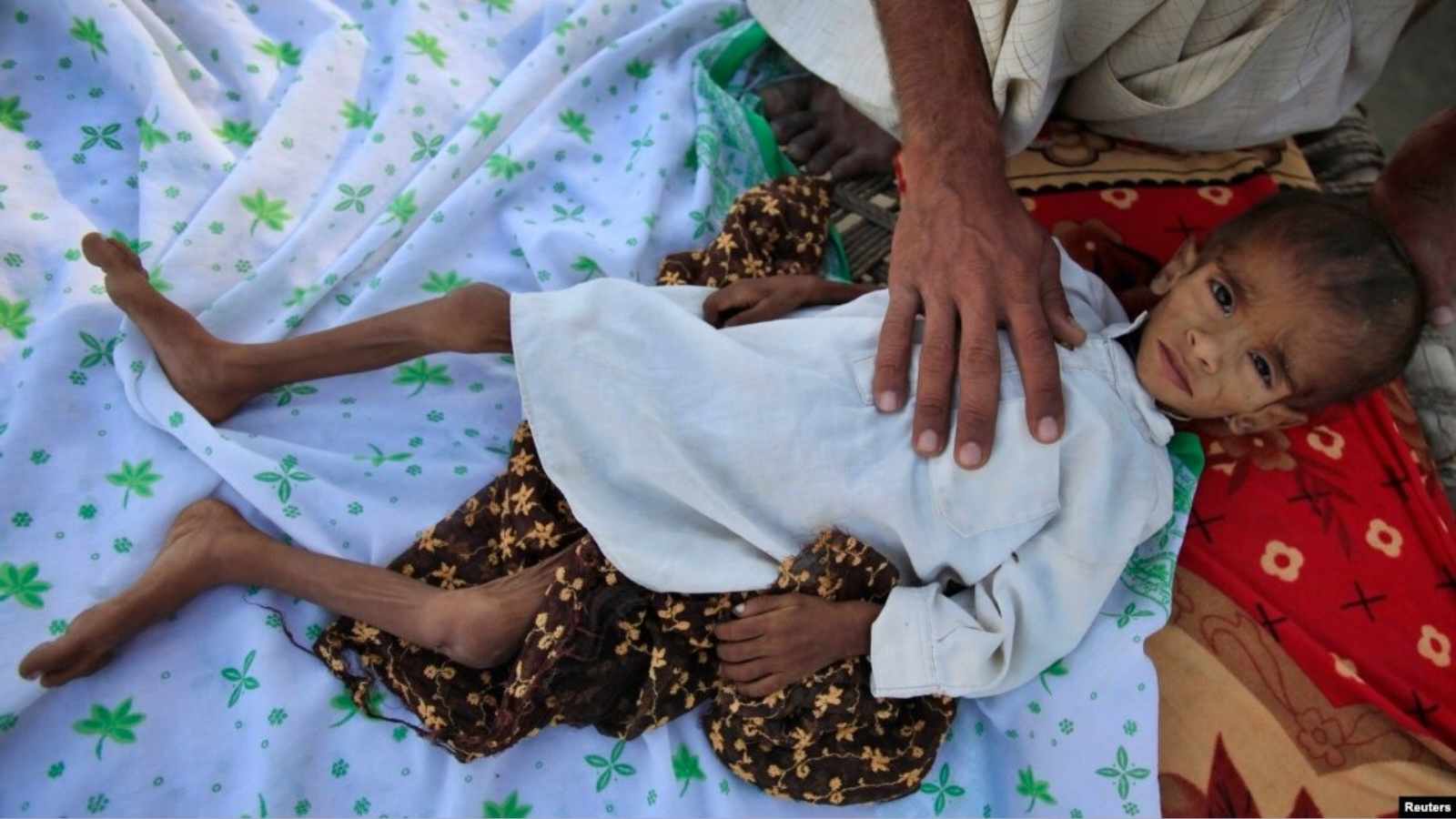
Although such changes have not yet been adopted by XDR S Typhi, the infectious disease specialist cautioned that “we are in real trouble” if they were. Researchers estimate that up to 20% of typhoid infections might be fatal if untreated, and there are now 11 million cases of typhoid per year.
Typhoid conjugate vaccines can help prevent future outbreaks to some extent, but if access to such vaccinations is not increased internationally, the entire globe could soon face another health disaster.
Read More: Scientists Discover Molecule That Kills Even The Deadliest Cancer: All You Need To Know
Read More: Chinese Scientists And Military Are Planning To Destroy Elon Musk’s Starlink Satellites Network